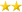Can Vitamin C supplements cause acute or chronic renal failure? Humans have evolved with very low intakes of vitamin C since the time their primate ancestors lost the ability to naturally synthesize it. Perhaps some people need less vitamin C than others and some people require more vitamin C?
http://www.chestjournal.org/cgi/content/full/118/2/561
Acute Renal Failure, Oxalosis, and Vitamin C Supplementation*
A Case Report and Review of the Literature
S. Mashour, MD; J. F. Turner Jr., MD, FCCP and R. Merrell, MD
* From the Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine (Drs. Mashour and Turner) and the Division of Nephrology (Dr. Merrell), Department of Medicine, University of Nevada School of Medicine, Las Vegas, NV.
Correspondence to: J. Francis Turner, Jr., MD, FCCP, Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, University of Nevada School of Medicine, 2040 W. Charleston, Suite 300, Las Vegas, NV 89102; e-mail: jturner@med.unr.edu
[...]
A 31-year-old African-American man presented to the emergency department at the University Medical Center with a 6-day history of headache and a 3-day history of nausea and vomiting. His history was otherwise unremarkable. He denied any recent travel or use of illicit medications, but admitted to the daily use of vitamin C (500 mg tablets, four to five tablets daily) purchased at a local health food store. The following results of physical examination were normal: sodium, 141 mEq/L; potassium, 4.5 mEq/L; chloride, 103 mEq/L; and CO2, 15 mEq/L. The BUN level was 22 mg/d, with a creatinine level of 10.1 mg/dL. A urinalysis showed 2+ protein, 2+ blood, and 0 to 2 WBCs per high-power field without crystals or eosinophils. The total creatine phosphokinase level was 72 U/L, with a serum osmolality of 303 mg/dL. The results of a quantitative toxicology screen for ethanol intoxication and ethylene glycol proved negative. Renal ultrasound revealed increased cortical echogenicity of the kidneys measuring 10 cm and 11.6 cm. A renal biopsy was performed on day 2 (Fig 1 ) and demonstrated acute tubular necrosis and massive oxalate deposition. Treatment with pyridoxine was started on hospital day 4 and was continued until day 9. On further inquiry, the patient was able to recall that he had begun taking even larger numbers of vitamin C tablets a few days prior to the onset of symptoms, up to 10 tablets daily (5,000 mg) due to a recent upper respiratory infection. Antinuclear antibody, antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody, and antistreptolysin O antibody titers were negative. Complement levels were within normal limits, and HIV serology was negative. The patient underwent two sessions of hemodialysis, with serial measurements of BUN and creatinine showing improvement in renal function. On day 14, measurements showed a BUN of 14 mg/dL and a creatinine level of 2.2 mg/dL; the patient was discharged home, with follow-up in his hometown.