Bernice E. Eddy, Ph.D., F.A.P.H.A., and Sarah E. Stewart, M.D., Ph.D.
https://ajph.aphapublications.org/doi/pdf/10.2105/AJPH.49.11.1486
Newborn mice,3 hamsters,4 and rats9 when injected with the virus subcutaneously react by the development of malignant neoplasms that in time kill the animals. Almost all mice develop parotid gland tumors and in addition tumors in other tissues. Twenty-six histologically different tumors have been observed. The virus induces multiple sarcomas and angiomatous lesions in the hamster and the commonest sites are the wall of the heart, liver, lungs, kidneys, and subcutaneous tissues. The most common tumors induced in the rat are sarcomas of the kidneys and subcutaneous tissues.
The "fraud" that is the Medical Medium works tells us that for most cancers, the root cause is a virus. The few exceptions include mesothelioma caused by asbestos. Thanks to pointers in the Ed Haslam book Dr. Mary's Monkey, we learn of the early NIH work of Drs. Eddy and Stewart (1950s) who first proved that simian (monkey) viruses induce cancers when they cross species.
The early Eddy/Stewart papers describe how the viruses were "cultured" and propagated.
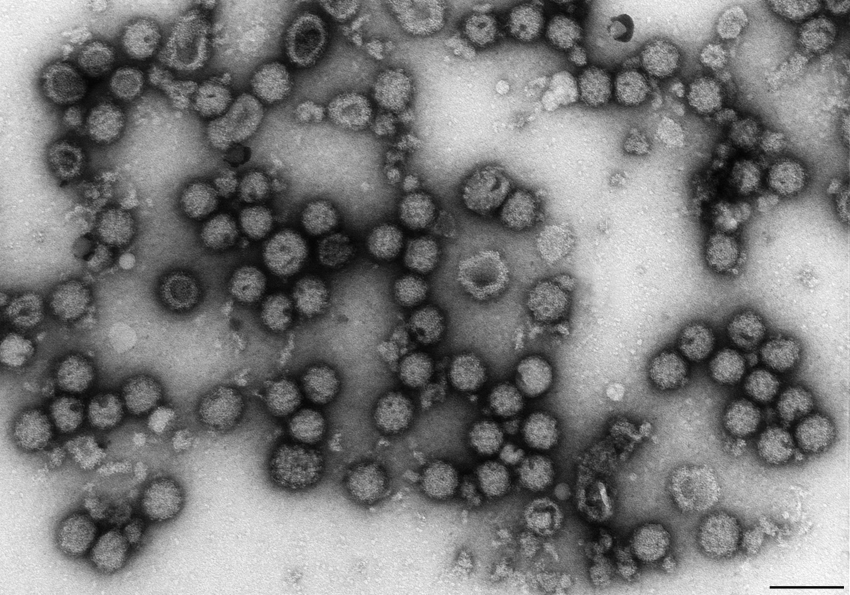
p. 1488
Passage of fhe SE Polyoma Virus Through Animals and Tissue Cultures
The SE polyoma virus has been passed from animal to animal and from one species to another with tissue cul- ture passage between each animal pass-age as shown in Table 2. All of the animals injected with the tissue culture- grown virus developed tumors with the exception of the two dwarfed mice that had received the virus at birth.
The 1959 Eddy/Stewart paper describes the routes of the virus
Routes of Injection of the SE Polyoma Virus
Tumors are routinely induced in animals by the introduction of virus subcutaneously in newborn animals. Work in progress indicates that tumors are induced in hamsters when virus is given either subcutaneously, intramus-cularly, intraperitoneally, or intracerebrally. The dose of virus given intra-cerebrally was 0.03 ml as compared to 0.2 ml doses by other routes; yet many of the animals developed tumors in about the same period of time. The route was less satisfactory for tests for tumor induction than other routes be-cause some animals died and no tumors could be detected macroscopically.
Propagation of the Virus
The first isolations of the virus were made by inoculating monkey kidney cell cultures that had grown out in sheets with either minced enlarged lymph glands, liver, and spleen or ex-tracts of these tissues. The tissue ex-tracts were prepared by grinding the weighed tissues with alundum, diluting with Earle's balanced salt solution' to make a 10 per cent suspension, and
centrifuging to remove the sediment.
To me one of the most surprising findings in this early research was the baking soda enhances the growth of the virus and cancers! This is surprising because of the line of reasoning that baking soda is anti-cancerous.
More recently variation in the amount of sodium bicarbonate in the medium has been shown to have a striking effect on cytopathogenicity5 and on propa- gation of the virus. This is shown in Table 1. When a low concentration of sodium bicarbonate (0.5 ml of 5 per cent sodium bicarbonate per 100 ml of medium) was present little virus was present in the tissue culture fluids and cytopathogenic changes were not pronounced. The same virus inoculum on the same cells but nourished with medium containing a higher concen- tration (1.0-3.5 ml of 5 per cent sodium bicarbonate per 100 ml of medium) gave rise to increasing cytopathogenic
changes and higher concentrations of the virus.
It is interesting that the Polyoma virus in this paper is now called the SV40 virus, to emphasize that there were 39 earlier simian (monkey) viruses discovered.
And it was the cancer-causing SV40 virus that was inadvertently included in the polio vaccines (grown on monkey kidneys) that caused the subsequent soft-tissue cancer epidemic in the baby boomers .